In this Article we will discuss about Characteristics of Western Educational Philosophy.
Introduction
Western educational philosophy has played a significant role in shaping modern education systems around the world. It focuses primarily on the development of intellectual abilities, critical thinking, and the acquisition of knowledge in various fields. While it has evolved over time, it has remained rooted in certain core principles such as individualism, rationality, and practicality.
Characteristics of Western Educational Philosophy
Below are some of the key characteristics of Western educational philosophy, explained in simple and easy-to-understand words.
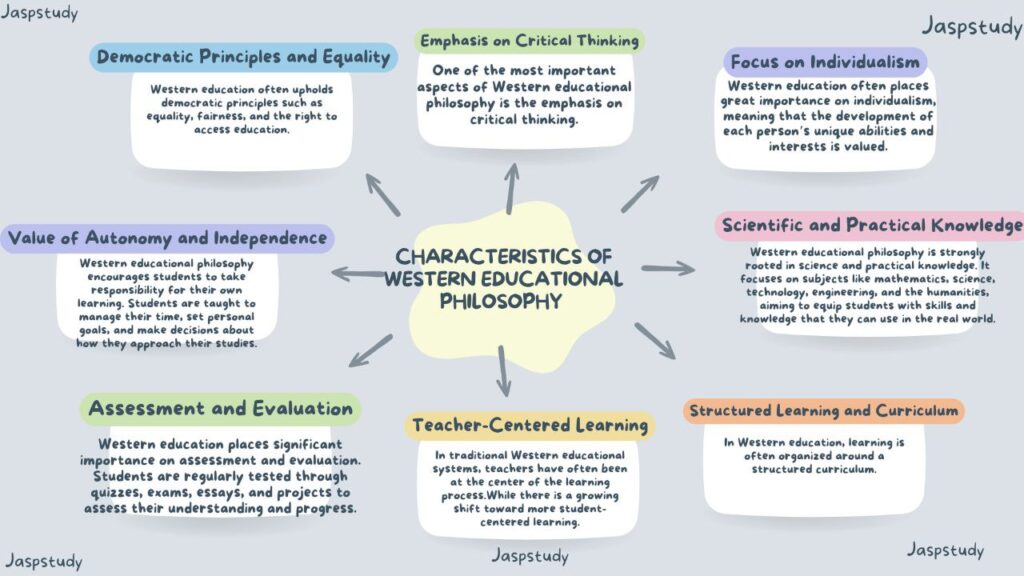
1. Emphasis on Critical Thinking
One of the most important aspects of Western educational philosophy is the emphasis on critical thinking. Critical thinking encourages students to question ideas, challenge assumptions, and analyze information deeply. Instead of memorizing facts, students are taught to think independently, solve problems, and make decisions based on logic and evidence. This encourages curiosity and the development of reasoning skills, helping students become more capable of understanding complex issues.
2. Focus on Individualism
Western education often places great importance on individualism, meaning that the development of each person’s unique abilities and interests is valued. It recognizes that each student has different talents, learning styles, and needs. Education is often personalized, allowing students to follow their own paths and make choices that align with their personal goals and strengths. This approach encourages self-expression, independence, and the belief that every person has the potential to succeed in their own way.
3. Scientific and Practical Knowledge
Western educational philosophy is strongly rooted in science and practical knowledge. It focuses on subjects like mathematics, science, technology, engineering, and the humanities, aiming to equip students with skills and knowledge that they can use in the real world. The emphasis is on the practical application of knowledge to solve problems and improve everyday life. This practical approach ensures that students are prepared for careers and challenges in a rapidly changing world.
4. Structured Learning and Curriculum
In Western education, learning is often organized around a structured curriculum. A curriculum outlines the subjects, skills, and knowledge that students are expected to learn at different stages of their education. It provides a clear framework for learning and sets specific goals for each grade level. This structure ensures that students progress in a systematic way, building on what they have learned in previous years. The curriculum is also designed to be flexible, allowing teachers to adapt to the needs of their students.
- Philosophy- Meaning, Definition,Nature And Branches
- Meaning Scope And Functions of Philosophy of Education
- Interrelationship Between Philosophy and Education
5. Teacher-Centered Learning
In traditional Western educational systems, teachers have often been at the center of the learning process. Teachers are seen as experts who guide students through the curriculum, deliver lessons, and provide feedback on student performance. The teacher’s role is to explain concepts, answer questions, and create an environment where students can engage with the subject matter. While there is a growing shift toward more student-centered learning, the teacher’s role as a facilitator of knowledge remains important in Western education.
6. Assessment and Evaluation
Western education places significant importance on assessment and evaluation. Students are regularly tested through quizzes, exams, essays, and projects to assess their understanding and progress. These assessments help measure how well students are learning and provide feedback to both students and teachers. Standardized testing is commonly used in many Western education systems to compare students’ performance and to track the effectiveness of educational programs. This focus on assessment helps identify areas where students need improvement and encourages accountability.
7. Value of Autonomy and Independence
Western educational philosophy encourages students to take responsibility for their own learning. Students are taught to manage their time, set personal goals, and make decisions about how they approach their studies. This development of autonomy and independence helps students become self-motivated, confident, and capable of making decisions on their own. It is believed that by learning to work independently, students become more prepared for life beyond school, including higher education and the workplace.
8. Democratic Principles and Equality
Western education often upholds democratic principles such as equality, fairness, and the right to access education. The idea is that every student, regardless of their background, should have the same opportunities to succeed. In many Western countries, education is free and compulsory for children, ensuring that everyone has the chance to learn. Additionally, education systems in the West emphasize the importance of freedom of expression, allowing students to share their ideas, ask questions, and engage in discussions.
9. Focus on Innovation and Creativity
Western educational philosophy encourages students to think creatively and develop innovative solutions to problems. Creativity is highly valued, especially in fields like the arts, design, and entrepreneurship. Students are encouraged to think outside the box, explore new ideas, and express themselves in unique ways. This focus on innovation helps students develop problem-solving skills and prepares them to meet the challenges of an ever-changing world.
10. Liberal Arts Education
Another characteristic of Western educational philosophy is the emphasis on liberal arts education. Liberal arts education aims to provide a well-rounded education by exposing students to a wide range of subjects, including literature, history, philosophy, mathematics, and the sciences. The goal is to develop students’ intellectual curiosity, cultural awareness, and critical thinking abilities. A liberal arts education helps students develop versatile skills that are useful in a variety of fields, preparing them for a broad range of careers and life experiences.
11. Emphasis on Research and Inquiry
In Western educational systems, research and inquiry are central components of the learning process. Students are often encouraged to conduct research, ask questions, and seek answers through investigation and analysis. Higher education, in particular, focuses heavily on research and scholarly inquiry, with students being trained to explore new ideas, test hypotheses, and contribute to the body of knowledge in their fields. This emphasis on research fosters a culture of intellectual curiosity and advances human understanding.
12. Technology Integration
In modern Western education, technology plays an important role in the learning process. Schools and universities integrate digital tools and resources into the classroom, using computers, the internet, and educational software to enhance learning. Technology helps students access information quickly, collaborate with others, and engage in interactive learning experiences. The use of technology in education prepares students for the digital world and the technological demands of the modern workforce.
13. Global Perspective and Diversity
Western education often promotes a global perspective by encouraging students to learn about different cultures, ideas, and ways of life. Many Western institutions offer programs that allow students to study abroad, interact with people from different countries, and develop a deeper understanding of global issues. This international outlook prepares students to work in diverse environments and helps them appreciate the richness of cultural diversity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Western educational philosophy is characterized by a focus on critical thinking, individualism, practical knowledge, and structured learning. It values autonomy, independence, and democratic principles while encouraging creativity, research, and innovation.
- Origin and Geographical Extent of Harappan civilization
- Main features of Mathura Style of kushana Sculptural Art
- Features of the Harappan civilisation
- Sailent features of the town planning of Harappan civilization
- Write a detailed note on Kayatha Culture and its salient features
- Write an essay on Jorwe Culture
- Main Features of Mauryan Art
- Discuss The Philosophy of History of Arnold Toynbee
- Date of coronaion of Kanishka1|Date of Accession of Kanishka 1