In this Article we will discuss about Group factor theory of Intelligence B.Ed notes.
Other Name- Thurstone’s theory : Primary mental abilities/Group factor theory
Group factor theory of Intelligence
Thurstone States that Intelligent Activities are not an expression of innumerable highly specific factors, as Thorndike claimed. Nor is it the expression primarily of a general factor that pervades all mental activities. It is the essence of intelligence, as Spearman held. Instead, the analysis of interpretation of Spearman and others led them to the conclusion that ‘certain’ mental operations have in common a ‘primary’ factor that gives them psychological and functional unity and that differentiates them from other mental operations. These mental operations then constitute a group.
A second group of mental operation has its own unifying primary factor, and so on. In other words, there are a number of groups of mental abilities, each of which has its own primary factor, giving the group a functional unity and cohesiveness. Each of these primary factors is said to be relatively independent of the others.
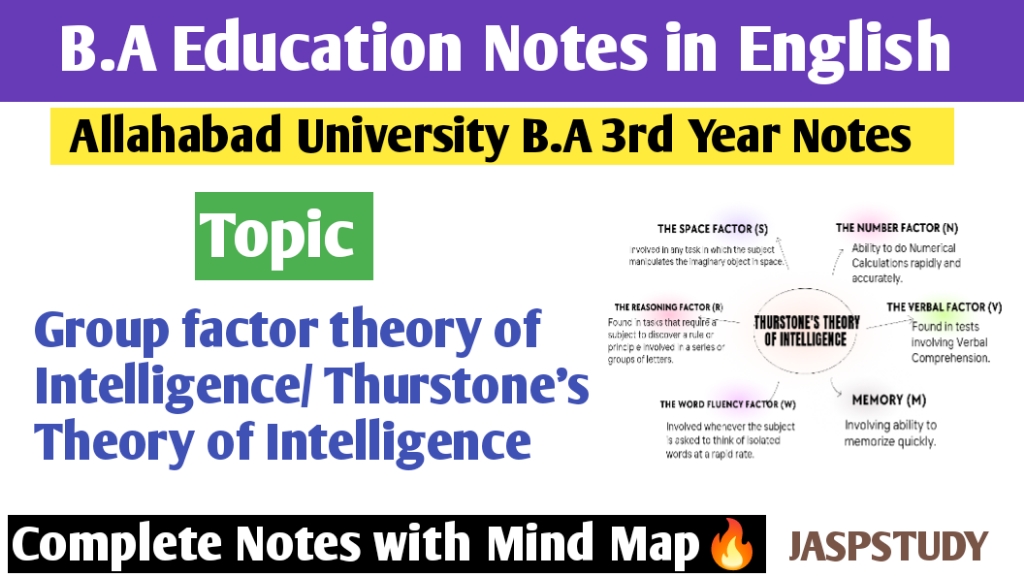
Factor

Thurstone has given the following six primary factors :
(i) The Number Factor (N)—Ability to do Numerical Calculations rapidly and accurately.
(ii) The Verbal Factor (V)—Found in tests involving Verbal Comprehension.
(iii) The Space Factor (S)—Involved in any task in which the subject manipulates the imaginary object in space.
(iv) Memory (M)—Involving ability to memorize quickly.
(v) The Word Fluency Factor (W)—Involved whenever the subject is asked to think of isolated words at a rapid rate.
(vi) The Reasoning Factor (R)—Found in tasks that require a subject to discover a rule or principle involved in a series or groups of
letters.
Based on these factors Thurstone constructed a new test of intelligence known as ‘‘Test of Primary Mental Abilities (PMA).’’
- Unifactor Theory and Two Factor Theory of Intelligence
- Meaning,Characteristics and Theories of Intelligence
- Characteristics of Indian Educational Philosophy
- Characteristics of Western Educational Philosophy
- Meaning Scope And Functions of Philosophy of Education
- Interrelationship Between Philosophy and Education
- Philosophy- Meaning, Definition,Nature And Branches
Thurstone’s Test of Primary Mental Abilities (PMA)
Based on these identified factors, Thurstone developed the Test of Primary Mental Abilities (PMA) to measure a person’s abilities in each of these six domains. The PMA test was designed to assess the individual primary factors, providing a more detailed picture of a person’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses compared to a general intelligence test. The PMA is significant because it marks a shift from the one-factor approach to intelligence, emphasizing multiple dimensions of mental ability that reflect a variety of cognitive functions.
In summary, Thurstone’s theory of primary mental abilities was a groundbreaking contribution to the field of psychometrics, offering an alternative to Spearman’s theory of general intelligence and providing a framework for understanding the complexities of human intelligence. His model highlighted the importance of distinguishing between different cognitive abilities, each contributing uniquely to overall intellectual performance.