In this post we will discuss about the Main Features of Ashokan Pillars.
Introduction
The Ashokan Pillars are a set of remarkable stone pillars built by Emperor Ashoka, one of India’s greatest rulers. Ashoka ruled the Maurya Empire from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. These pillars are important because they not only showcase advanced architecture and art from ancient India, but they also carry messages about Ashoka’s rule and his promotion of Buddhism. The Ashokan Pillars stand as a symbol of his commitment to peace, justice, and moral values.
Main Features of Ashokan Pillars
Let’s explore the main features of these famous pillars.
1.Purpose of the Pillars
The Ashokan Pillars were primarily built to spread the teachings of Emperor Ashoka and his support for Buddhism. After the Kalinga War, which caused a lot of suffering, Ashoka adopted Buddhism as his guiding philosophy. He wanted to promote peace, kindness, and non-violence. To achieve this, he placed these pillars in different parts of his empire. The inscriptions on the pillars carried messages about moral behavior, justice, and Buddhism. Ashoka used the pillars to encourage people to follow righteous paths in life.
2.Materials Used
The Ashokan Pillars are made from Red sandstone, which was a common material used in ancient India for building structures. The sandstone was carefully selected for its durability and ease of carving. The pillars were polished to a smooth finish, making them stand out in their surroundings. Some of the pillars also had a polished appearance that made them shine in the sunlight. The stone used for these pillars came from quarries that were located in places like Chunar and Mirzapur, which were known for their high-quality sandstone.
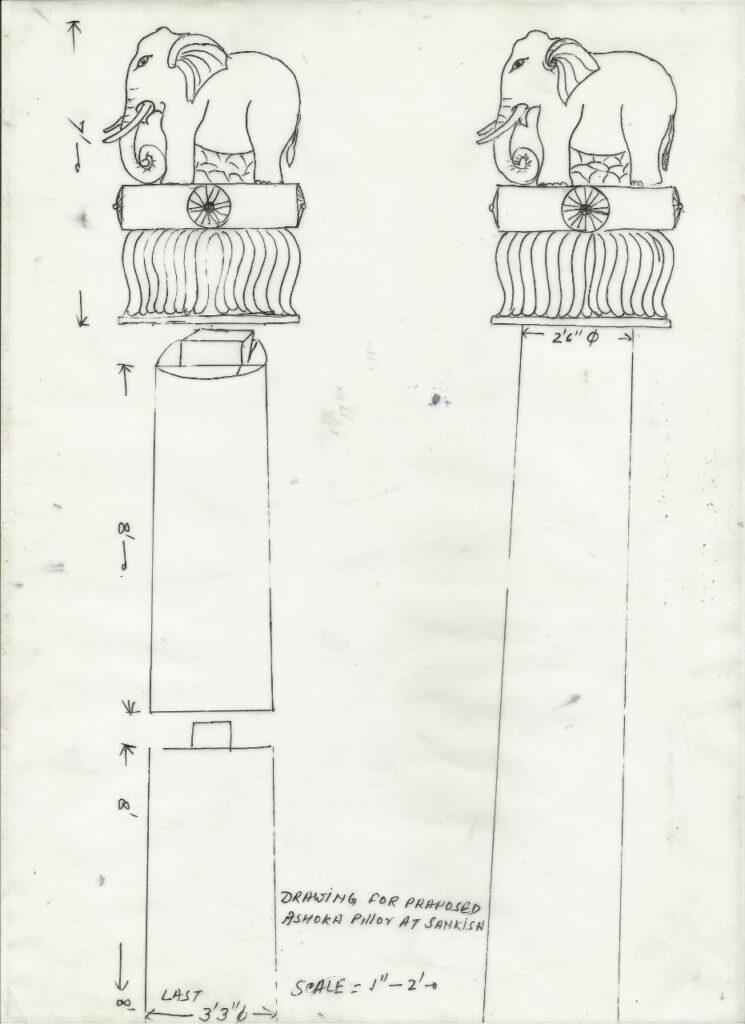
3.Design and Shape
The Ashokan Pillars are tall and slender, with an average height of about 12 to 15 meters (39 to 49 feet). The pillars taper slightly as they rise, making them look even more impressive. Most of the pillars were topped with sculptures of animals, such as lions, elephants, or bulls, which were symbolic of power, strength, and protection. These sculptures, often called “capital animals,” are one of the most famous features of the Ashokan Pillars.
The pillar itself is a smooth, cylindrical shaft with a square base. The upper part of the pillar is generally more decorative, with carvings of animals or other symbols. The capitals (tops of the pillars) were sometimes adorned with elaborate carvings, showcasing the craftsmanship and artistic skills of the time.
- Origin and Geographical Extent of Harappan civilization
- Main features of Mathura Style of kushana Sculptural Art
- Features of the Harappan civilisation
- Sailent features of the town planning of Harappan civilization
- Write a detailed note on Kayatha Culture and its salient features
- Write an essay on Jorwe Culture
- Main Features of Mauryan Art
- Discuss The Philosophy of History of Arnold Toynbee
- Date of coronaion of Kanishka1|Date of Accession of Kanishka 1
4.The Inscriptions
One of the most important features of the Ashokan Pillars is the inscriptions that are carved into the stone. These inscriptions were written in different scripts, including Brahmi and Kharosthi. The inscriptions often carried messages of Ashoka’s policies, his conversion to Buddhism, and his thoughts on peace, morality, and governance. They were intended to guide the people of the empire and promote good conduct.
The inscriptions on the Ashokan Pillars are in the form of edicts (official messages). These edicts are divided into two categories: major and minor. The major edicts, which are longer, contain Ashoka’s rules about non-violence, kindness to animals, respect for elders, and religious tolerance. The minor edicts are shorter and focus more on moral teachings and ethical behavior.
The most famous of these inscriptions are the Edicts of Ashoka, which are considered to be some of the oldest written records of Indian history. These inscriptions provide a detailed account of Ashoka’s thoughts on governance, social welfare, and his effort to create a just and peaceful society.
5.Location of the Pillars
The Ashokan Pillars were placed in different parts of the Maurya Empire. These pillars were strategically placed in locations where they would be seen by a large number of people. Some of the most well-known locations where Ashokan Pillars have been found include Sarnath,Lauriya Nandangarh, Delhi-Topra, and Rampurva. The Sarnath pillar, for example, is especially significant because it marks the place where Buddha gave his first sermon.
This pillar, with its famous lion capital, is now the national emblem of India.
The placement of these pillars in important towns and cities helped spread Ashoka’s message across the empire. The pillars served as a reminder to the people to follow Ashoka’s teachings and embrace the principles of Buddhism.
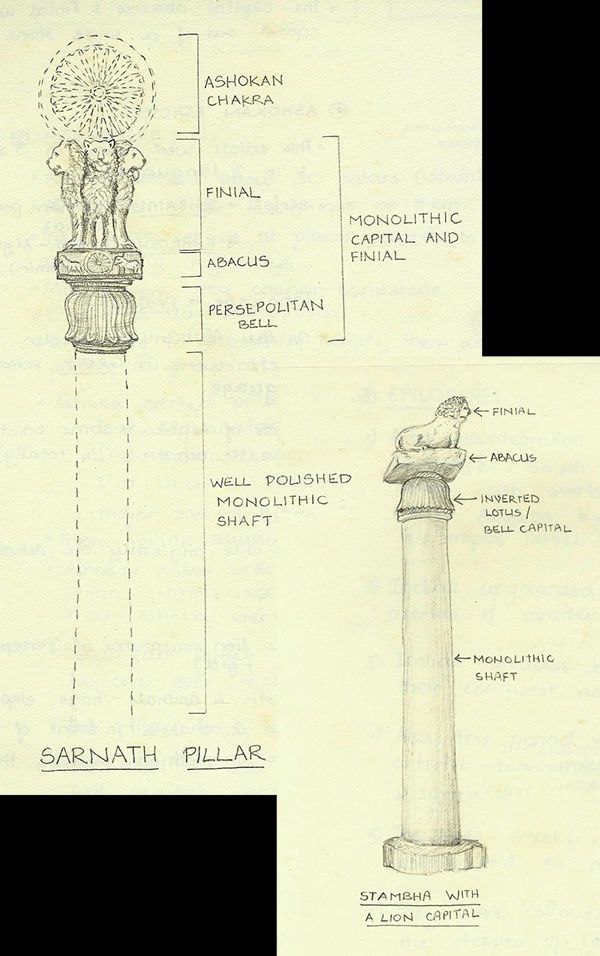
6.The Lion Capital of Ashoka
One of the most iconic features of the Ashokan Pillars is the Lion Capital. The Lion Capital is a sculpture that sits atop several of Ashoka’s pillars, including the famous one at Sarnath. The Lion Capital features four lions standing back-to-back, symbolizing the Buddha’s teachings spreading in all directions. These lions are often thought to represent courage, power, and authority.
The Lion Capital also has other important features. Beneath the lions, there is a wheel (known as the Dharma Chakra), which symbolizes the teachings of the Buddha and the cycle of life. The wheel has 24 spokes, which represent the 24 hours in a day, signifying that the teachings of the Buddha are eternal. Below the wheel, there is a bell-shaped structure, which also represents the wheel of law, emphasizing the spread of Dharma (righteousness).
The Lion Capital from the Sarnath pillar became one of the most important national symbols of India, and it is prominently featured on India’s national flag and emblem.
7.Symbolism of the Pillars
The Ashokan Pillars are rich in symbolism. They represent not only Ashoka’s rule but also the values of Buddhism, such as non-violence, peace, and compassion. The presence of animal sculptures on the top of many pillars symbolizes power, guardianship, and the protection of the Buddha’s teachings. The wheel of Dharma on the Lion Capital signifies the law of Buddhism and its path to enlightenment.
The smooth, polished surface of the pillars also represents purity, while the inscriptions speak to the moral and ethical values that Ashoka promoted. These pillars were meant to remind people of the importance of moral conduct, religious tolerance, and kindness.
8.Influence and Legacy
The Ashokan Pillars had a lasting impact on Indian art and architecture. They introduced a new style of stone carving and sculpture that influenced later Indian dynasties. The lion capital of Ashoka became an important symbol of Indian culture and history, and the values he promoted continue to be an integral part of Indian society.
The pillars also reflect Ashoka’s commitment to spreading the teachings of Buddhism. They stand as a testament to his transformation from a warrior king to a ruler who valued peace, compassion, and the well-being of his people. Ashoka’s efforts to spread Buddhism through the pillars helped the religion grow across India and beyond.
Conclusion
The Ashokan Pillars are significant historical and cultural monuments that reflect the values of Emperor Ashoka’s reign. These pillars are known for their design, the inscriptions carved into them, and the animal capitals that sit on top. The pillars were not just architectural feats but also tools for promoting peace, kindness, and Buddhism across the empire. Today, the Ashokan Pillars continue to be a powerful reminder of the moral teachings of one of India’s greatest emperors, and they remain an important part of India’s cultural heritage.
- Achievements of Kanishka
- Achievement of Pushyamitra Sunga
- Military Campaigns of Samudragupta| Conquest of Samudragupta
- Career and achievements of Julius Caesar|contributions of Julius Caesar
- Intellectual Achievement of Egyptian Civilization
- Salient Features Of Sumerian Civilization
- Salient features of Assyrian Civilization
- Rise of Magadha Empire from Bimbisara to Mahapadmananda
- Achievements of Mahapadmananda
- Main features of Bharhut Stupa
- Salient features of Vedic Culture
- Difference between Mathura and Gandhar School of Art

