In this Article we will Discuss about Characteristics of Indian Educational Philosophy.
Introduction
Indian educational philosophy has deep roots in the culture and history of India, shaped over thousands of years. It is not just about gaining knowledge, but also about learning life skills, developing values, and growing spiritually. The focus is on the overall development of a person, which includes the mind, body, and spirit.
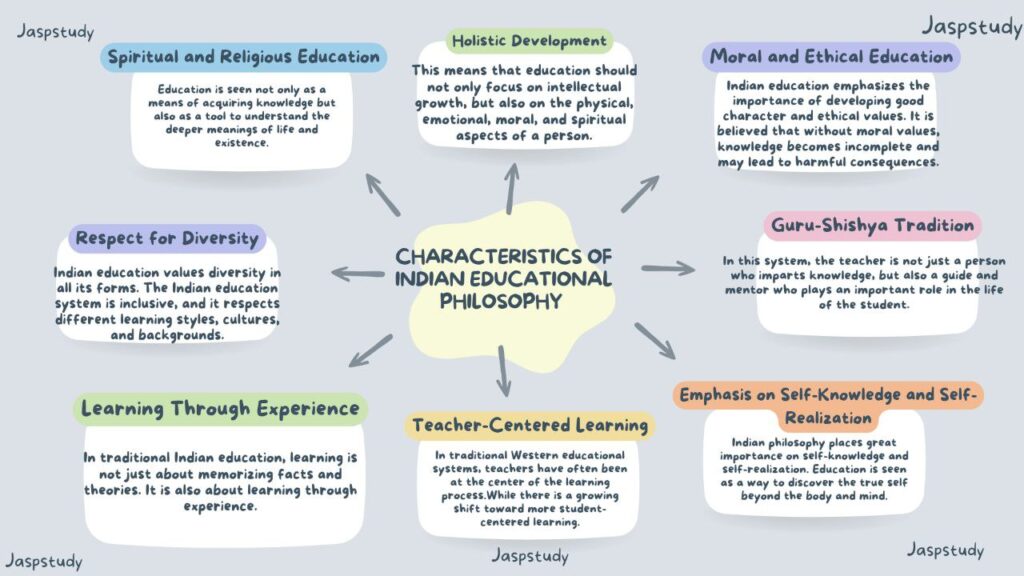
Characteristics of Indian Educational Philosophy
Below are some key characteristics of Indian educational philosophy, explained in simple and easy-to-understand words.
1. Holistic Development
One of the main characteristics of Indian educational philosophy is its focus on holistic development. This means that education should not only focus on intellectual growth, but also on the physical, emotional, moral, and spiritual aspects of a person. The goal is to help students become well-rounded individuals, capable of making a positive impact in the world. Education is seen as a tool to create harmony within oneself and with others.
2. Moral and Ethical Education
Indian education emphasizes the importance of developing good character and ethical values. It is believed that without moral values, knowledge becomes incomplete and may lead to harmful consequences. Education is seen as a means of teaching values such as truth, honesty, kindness, non-violence (ahimsa), and respect for others. Indian philosophy believes that a strong moral foundation is essential for building a better society. Teachers encourage students to not only learn academic subjects but also to practice good conduct and compassion in their daily lives.
3. Guru-Shishya Tradition
A unique feature of Indian education is the Guru-Shishya (teacher-student) tradition. In this system, the teacher is not just a person who imparts knowledge, but also a guide and mentor who plays an important role in the life of the student. The relationship between the guru (teacher) and shishya (student) is personal and close. The guru helps the student not only with academic learning but also with life skills and spiritual guidance. This system, which has existed since ancient times, emphasizes learning through direct interaction with the teacher and the sharing of wisdom.
- Philosophy- Meaning, Definition,Nature And Branches
- Meaning Scope And Functions of Philosophy of Education
- Interrelationship Between Philosophy and Education
- Characteristics of Western Educational Philosophy
4. Emphasis on Self-Knowledge and Self-Realization
Indian philosophy places great importance on self-knowledge and self-realization. Education is seen as a way to discover the true self beyond the body and mind. The ultimate goal of education is to understand one’s true nature and purpose in life. This spiritual dimension of education is reflected in ancient texts like the Upanishads and Bhagavad Gita, which focus on understanding the self and the universe. Indian education teaches that true wisdom comes from knowing oneself, and it encourages students to reflect on their inner being to achieve spiritual growth.
5. Learning Through Experience
In traditional Indian education, learning is not just about memorizing facts and theories. It is also about learning through experience. Students were encouraged to learn from the world around them, through observation and participation in daily life. This could include learning from nature, learning through stories, or gaining wisdom from personal experiences. This approach makes learning more meaningful and allows students to understand concepts in a practical way. Experiential learning helps students to develop critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and creativity.
6. Respect for Diversity
Indian education values diversity in all its forms. The Indian education system is inclusive, and it respects different learning styles, cultures, and backgrounds. It recognizes that every individual is unique and may learn in different ways. Indian philosophy believes that each person has their own strengths and talents, and education should cater to these differences. This respect for diversity ensures that everyone has the opportunity to succeed, no matter their background or learning ability. It teaches students to value and appreciate differences in others.
7. Spiritual and Religious Education
In Indian educational philosophy, spirituality and religion play a central role. Education is seen not only as a means of acquiring knowledge but also as a tool to understand the deeper meanings of life and existence. Religious teachings, especially from Hinduism, Buddhism, and other Indian traditions, form an essential part of the curriculum. Students are taught spiritual wisdom, meditation, and mindfulness to help them achieve inner peace and balance. The belief is that spiritual growth is just as important as intellectual development.
8. Teacher as a Role Model
In Indian education, the teacher is not just someone who imparts knowledge but is also seen as a role model for students. The teacher’s actions, behavior, and attitudes are carefully observed by the students, who learn by imitating their teacher. Teachers are expected to lead by example, showing qualities such as patience, humility, discipline, and kindness. This is a key part of the Guru-Shishya tradition, where the teacher’s character has a lasting influence on the student’s life.
9. Focus on Righteous Living (Dharma)
Indian philosophy emphasizes living a life of dharma, which refers to righteous living and fulfilling one’s duties in the right way. Education is seen as a means of teaching students how to live in accordance with dharma, which includes respecting others, acting with integrity, and contributing positively to society. By following dharma, students are taught to make choices that align with truth, justice, and morality.
10. Focus on Logic and Reasoning
Along with spiritual and moral education, Indian educational philosophy also encourages logical thinking and reasoning. Ancient Indian philosophers, such as Aryabhata and Chanakya, made significant contributions to subjects like mathematics, astronomy, and political science. Logical reasoning and analytical thinking were highly valued in ancient Indian education, and this tradition continues to be important in modern education as well. Indian philosophy teaches students to question, reason, and think critically about the world around them.
11. Non-Competitive Learning
Indian educational philosophy does not emphasize competition in the same way as many modern education systems do. Instead, the focus is on individual growth and learning at one’s own pace. While it is important to strive for excellence, the emphasis is on personal improvement and collaboration rather than comparison with others. Students are encouraged to work together, help each other, and share knowledge, creating a learning environment based on cooperation and mutual respect.
12. Lifelong Learning
In Indian philosophy, education is considered a lifelong journey. It is not confined to the classroom or limited to a certain age. The belief is that learning should continue throughout one’s life. From childhood to old age, every stage of life provides an opportunity for learning and self-improvement. The concept of Jnana (knowledge) and Vijnana (wisdom) is seen as something that grows over time, and it is never complete. This encourages a mindset of curiosity and growth, where individuals continue to learn and evolve throughout their lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Indian educational philosophy is based on a holistic approach that emphasizes intellectual, emotional, moral, and spiritual development. It focuses on character building, learning through experience, and discovering one’s true self. Indian education values respect for diversity, the importance of values, and the role of the teacher as a mentor and role model. It encourages students to live a righteous life, think critically, and pursue lifelong learning. Indian educational philosophy aims to create well-rounded individuals who contribute positively to society while growing in wisdom and knowledge.
- Origin and Geographical Extent of Harappan civilization
- Main features of Mathura Style of kushana Sculptural Art
- Features of the Harappan civilisation
- Sailent features of the town planning of Harappan civilization
- Write a detailed note on Kayatha Culture and its salient features
- Write an essay on Jorwe Culture
- Main Features of Mauryan Art
- Discuss The Philosophy of History of Arnold Toynbee
- Date of coronaion of Kanishka1|Date of Accession of Kanishka 1